In this section we discuss shape parameters grains that depend on one dimensional projections, i.e.,
|
caliper or Feret diameter in µm |
diameter in µm |
In order to demonstrate these parameters we first import a small sample data set.
% load sample EBSD data set
mtexdata forsterite silent
% reconstruct grains, discard boundary grains and smooth them
[grains, ebsd.grainId] = calcGrains(ebsd('indexed'),'angle',5*degree,'minPixel',5);
grains(grains.isBoundary) = [];
grains = smooth(grains('indexed'),10,'moveTriplePoints');
% plot all grains and highlight a specific one
plot(grains)
ind = 654;
hold on
plot(grains(ind).boundary,'lineWidth',5,'linecolor','blue')
hold off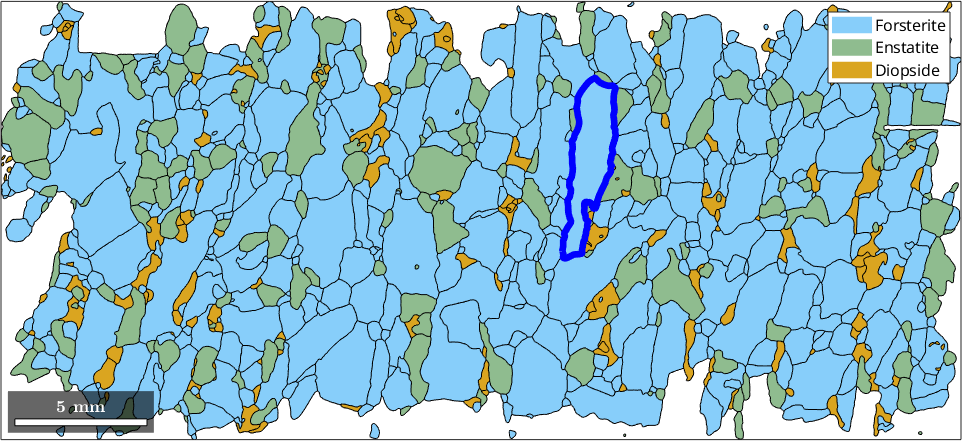
The most well known projection based parameter is the diameter which refers to the longest distance between any two boundary points and is given in µm.
grains(ind).diameterans =
6.9276e+03The diameter is a special case of the caliper or Ferret diameter of a grain. By definition the caliper is the length of a grain when projected onto a line. We may trace the caliper with respect to projection direction
close all
omega = linspace(0,180);
dir = vector3d.byPolar(90*degree,omega*degree);
plot(omega,grains(ind).caliper(dir),'LineWidth',2)
ylabel('length in \(\mu\)m','Interpreter','latex')
xlabel('angle of the projection line in degree')
xlim([0,180])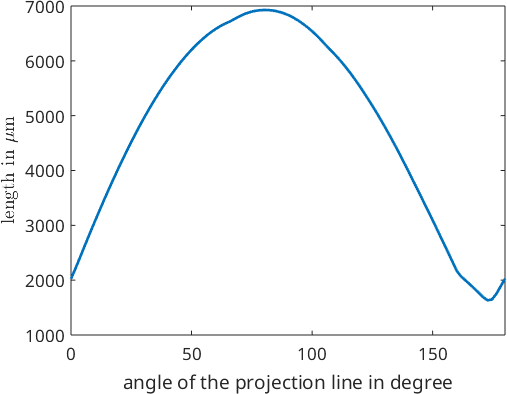
We observe that that maximum caliper is about 7000 while the minimum caliper is about 2000. We may compute the exact direction and length of the maximum or minimum by passing the options 'longest' or 'shortest' to the function caliper. In this case the the output is of type vector3d indicating the direction. The norm of the vector coincides with the caliper for this projection direction. Hence, the norm(grains.caliper('longest')) coincides with the diameter.
plot(grains(ind),'micronbar','off')
legend('off')
norm(grains(ind).caliper('longest'))
norm(grains(ind).caliper('shortest'))
hold on
quiver(grains(ind),grains(ind).caliper('longest'),'noScaling')
quiver(grains(ind),grains(ind).caliper('shortest'),'noScaling')
hold offans =
6.9276e+03
ans =
1.6308e+03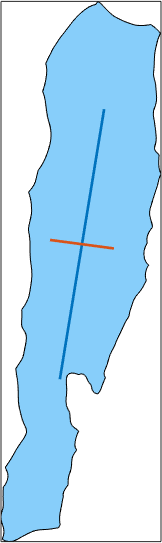
The difference between the longest and the shortest caliper can be taken as a measure how round a grain is.
cMin = grains.caliper('shortest');
cMax = grains.caliper('longest');
plot(grains,(norm(cMax) - norm(cMin))./norm(cMax),'micronbar','off')
mtexColorbar('title','c_{max} - c_{min}')
This longest and shortest caliper are comparable to grains.longAxis and grains.shortAxis computed from an ellipse fitted to the grain. In the case of rectangular particles, one might not primarily be interested in the longest caliper of a grain but rather in the direction normal to the shortest caliper. This is computed when specifying the option 'shortestPerp'. If we imagine a very strong alignment of the long axes of orthorhombic particles, the maximum diameter may show a bimodal distribution (the two, roughly equally distributed diagonals of the particle).
% load some test grains
testgrains = mtexdata('testgrains');
testgrains = smooth(testgrains([6 8]),10);
% compute the longest caliper and the caliper perpendicular to the shortest
cMax = testgrains.caliper('longest');
cMinPerp = testgrains.caliper('shortestPerp');
% plot the grains and visualize the different long axes
plot(testgrains,'micronbar','off','lineWidth',2)
hold on
quiver(testgrains,cMax,'DisplayName','longest calliper','LineWidth',3)
quiver(testgrains,testgrains.longAxis,'DisplayName','long axis','LineWidth',3)
quiver(testgrains,cMinPerp,'DisplayName','perp to shortest','LineWidth',3)
hold off
legend('Location','east')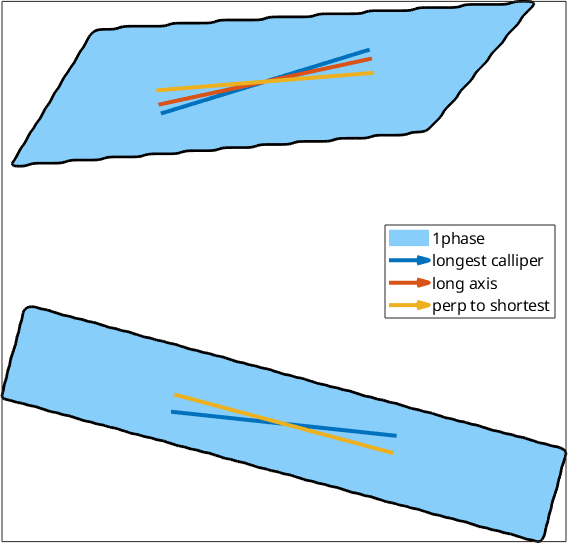
PAROR and SURFOR
Another way of quantifying shape fabrics is by making use of the cumulative projection function of the grains or the grain boundary segments. These methods are heavily inspired by Edwin A. Abbotts 'Flatland - A romance of many dimensions' (1884) and based on Panozzo, R., 1983, "Two-dimensional analysis of shape fabric using projections of digitized lines in a plane". Tectonophysics 95, 279-294. and Panozzo, R., 1984, "Two-dimensional strain from the orientation of lines in a plane." J. Struct. Geol. 6, 215-221. implemented in MTEX as grains.paror and grainBoudnary.surfor
As mentioned above the function caliper can be called with a list of angles and returns the projection length of all grains with respect to all angles.
% projection angle
omega = linspace(0,360*degree,361);
dir = vector3d.byPolar(90*degree,omega);
c = grains('Fo').caliper(dir);
subplot(1,2,1)
polarplot(omega,c,'LineWidth',2,'color',[0 0.25 0.5 0.25])
title('Forsterite')
% take the average
hold on
polarplot(omega,5*mean(c),'LineWidth',3,'color','k');
hold off
subplot(1,2,2)
c = grains('Enstatite').caliper(dir);
polarplot(omega,c,'LineWidth',2,'color',[0 0.25 0.5 0.25])
title('Enstatite')
% take the average
hold on
polarplot(omega,5*mean(c),'LineWidth',3,'color','k');
hold off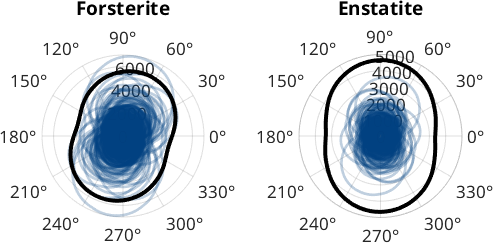
The above averaged caliper can be computed more directly by the function grains.paror which returns the cumulative particle projection function normalized to 1. The projection angles can be regarded as the rotation angle of the particle (counterclockwise) while projecting from the y-axis onto the x-axis.
close all
cumplF = paror(grains('fo'),omega);
cumplE = paror(grains('en'),omega);
plOpt = {'LineWidth',3,'color','k'};
subplot(2,2,1)
plot(omega/degree,cumplF,plOpt{:}); xlim([0 180]);
title('paror Forsterite')
subplot(2,2,2)
polarplot(omega,cumplF,plOpt{:})
subplot(2,2,3)
plot(omega/degree,cumplE,plOpt{:}); xlim([0 180]);
title('paror Enstatite')
subplot(2,2,4)
polarplot(omega,cumplE,plOpt{:})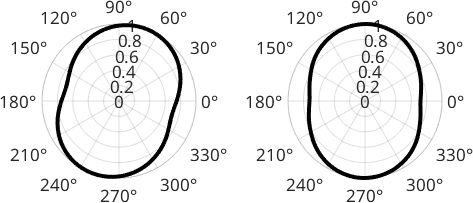
We can interpret the results in the following way. The minimum of the curve is a measure of the amplitude of the projection function and can be compared to an averaged axial ratio \(b/a\) of the entire fabric; isotropic fabrics would have a \(b/a\) close to 1 while highly anisotropic fabrics can be identified by small \(b/a\) values.
min(cumplF), min(cumplE)ans =
0.7102
ans =
0.7203The position of the maxima and minima of the projection function derived from paror can be interpreted in the following way: the maximum position represents the preferred axis parallel to the longest projection and the normal the minimum position represents the preferred axis related to the normal to the shortest projection function.
% using S1Fun for the Forsterite
sF_Fo = S1FunHarmonic.interpolate(omega,cumplF);
[~, maxposfo] = max(sF_Fo);
[~, minposfo] = min(sF_Fo);
[mod(maxposfo,pi) mod(minposfo-pi/2,pi)] /degree
% for the Enstatite
sF_Fo = S1FunHarmonic.interpolate(omega,cumplE);
[~, maxposfo] = max(sF_Fo);
[~, minposfo] = min(sF_Fo);
[mod(maxposfo,pi) mod(minposfo-pi/2,pi)]/degree
% or finding maxima and minima
% for the Forsterite
[~, id_max] = max(cumplF);
[~, id_min] = min(cumplF);
[mod(omega(id_max)./degree,180) mod(omega(id_min)./degree-90,180)]
% for the Enstatite
[~, id_max] = max(cumplE);
[~, id_min] = min(cumplE);
[mod(omega(id_max)./degree,180) mod(omega(id_min)./degree-90,180)]ans =
71.1000 74.4250
ans =
87.8250 88.5250
ans =
71.0000 74.0000
ans =
87.0000 88.0000The smaller the difference between these values, the closer the fabric is to an orthorhombic symmetry.
Similarly to using the entire particle (the convex hull in case of the projection functions), we can use a distribution of lines grainBoudnary.surfor. This can be useful for the quantification of the grain boundary anisotropy or in general might be needed if we look at boundaries which do not form closed outlines, e.g. a list of subgrain or twin boundaries or the contact between certain phases.
Let's compare the boundaries between the different unlike phases and between forsterite-forsterite in our sample:
close all
pairs = [1 1; nchoosek(1:3,2)];
phase = {'Fo' 'En' 'Di'};
for i=1:length(pairs)
gB = grains.boundary(phase{pairs(i,:)});
polarplot(omega, surfor(gB,omega), 'linewidth',2, ...
'DisplayName',[phase{pairs(i,1)} '-' phase{pairs(i,2)}]);
hold on
end
hold off
legend('Location','southoutside','Orientation','horizontal')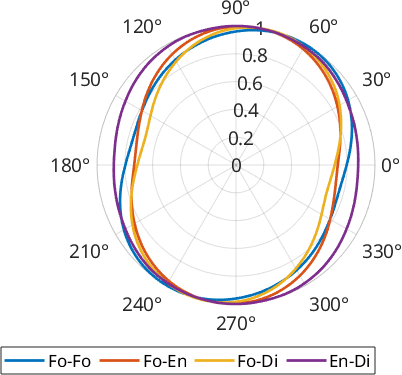
We can see that Forsterite-Forsterite boundaries form a fabric slightly more inclined with respect to the other phase boundaries and that the phase boundaries between the two pyroxenes (Enstatite and Diopside) show the lowest anisotropy.
Characteristic Shape
The characteristic shape results from the cumulative sum of all grain boundary segments ordered by the angle of the segment direction. It can be regarded as to represent the average grain shape, however without the need to use closed areas such as it would be required when working with grains.
Here we can compare the shape defined by Forsterite-Forsterite, Enstatite-Enstatite and Forsterite-Enstatite boundaries
plotopts = {'normalize','linewidth',2, 'plain'};
shapeF = characteristicShape(grains.boundary('f','f'))
plot(shapeF,plotopts{:})
hold on
shapeE = characteristicShape(grains.boundary('En','En'));
plot(shapeE,plotopts{:},'DisplayName','En-En')
hold on
shapeEF = characteristicShape(grains.boundary('En','Fo'));
plot(shapeEF,plotopts{:},'DisplayName','En-Fo')
hold off
legend('Location','southoutside','Orientation','horizontal')shapeF = shape2d
vertices: 1024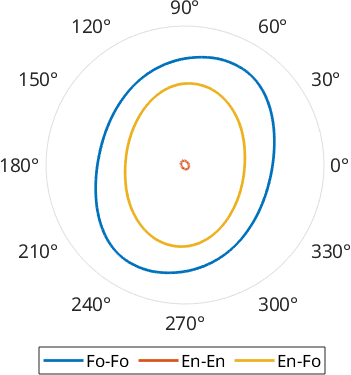
The output of characteristicShape is a shape2d object which behaves very similar to a grain2d object, hence it is easy to derive things such as a long axis or e.g. the angle between the longest and the shortest caliper which can be regarded as a measure of asymmetry.
angle(shapeF.caliper('longest'),shapeF.caliper('shortest')) / degree
angle(shapeE.caliper('longest'),shapeE.caliper('shortest')) / degree
angle(shapeEF.caliper('longest'),shapeF.caliper('shortest')) / degreeans =
78.7774
ans =
86.8311
ans =
79.7408