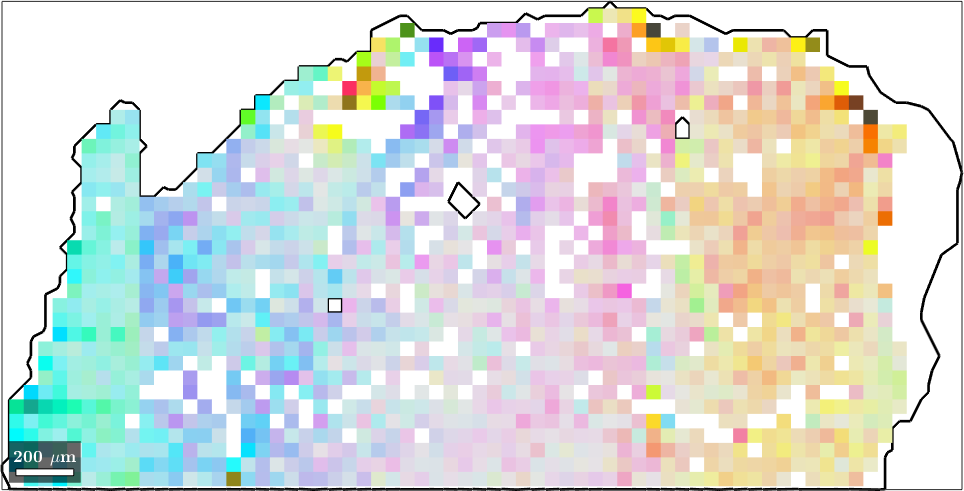
In this section we discuss color keys that are particular useful when analyzing data with very small deviation in orientation. Let us consider the following calcite data set
mtexdata sharp
ipfKey = ipfColorKey(ebsd);
plot(ebsd,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd.orientations))ebsd = EBSD (y↑→x)
Phase Orientations Mineral Color Symmetry Crystal reference frame
0 32 (0.16%) notIndexed
1 20119 (100%) calcite LightSkyBlue -3m1 X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
Scan unit : um
X x Y x Z : [0, 200] x [-100, 0] x [0, 0]
Normal vector: (0,0,1)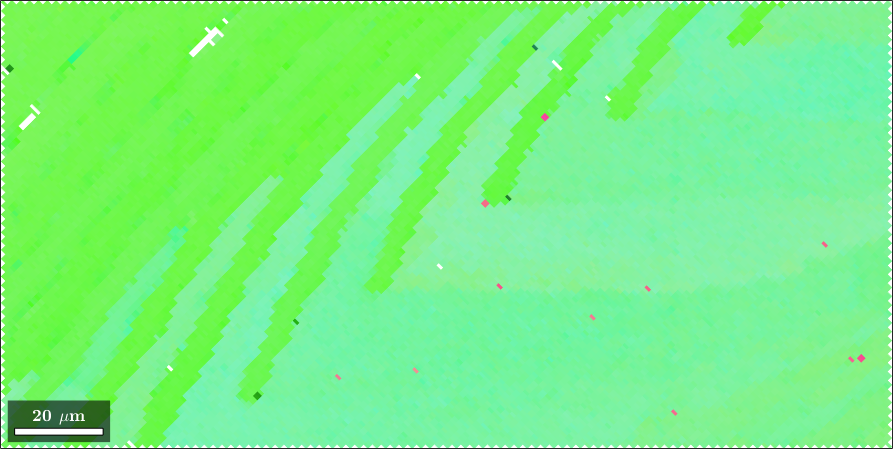
and have a look into the 101 inverse pole figure.
r = vector3d(1,0,1);
% compute the positions in the inverse pole figure
h = ebsd.orientations .\ r;
h = project2FundamentalRegion(h);
% compute the azimuth angle in degree
color = h.rho ./ degree;
plotIPDF(ebsd.orientations,r,'property',color,'MarkerSize',3,'grid')
mtexColorbarI'm plotting 8333 random orientations out of 20151 given orientations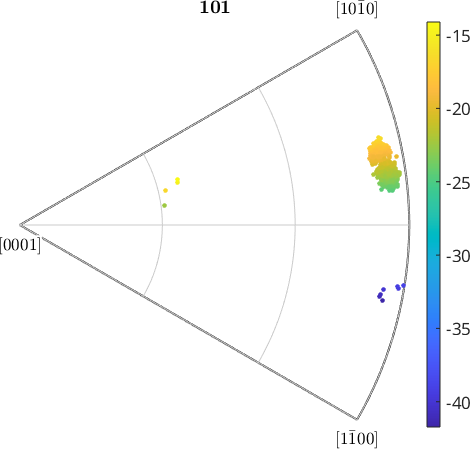
We see that all individual orientations are clustered around azimuth angle -20 degrees with some outliers at -35 degree. In order to increase the contrast for the main group, we restrict the color range from 110 degree to 120 degree.
setColorRange([-25 -15]);
% by the following lines we colorize the outliers in purple.
cmap = colormap;
cmap(end,:) = [1 0 1]; % make last color purple
cmap(1,:) = [1 0 1]; % make first color purple
colormap(cmap)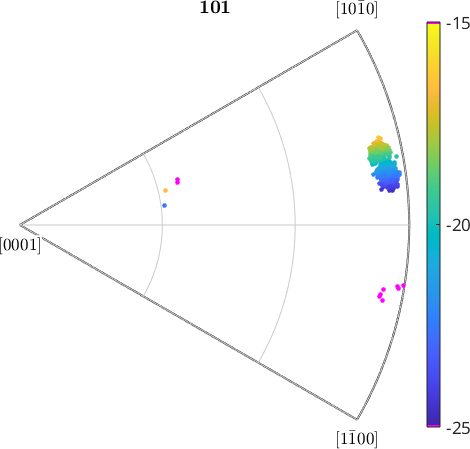
The same color coding we can now apply to the EBSD map.
% plot the data with the customized color
plot(ebsd,color)
% set scaling of the angles to 110 - 120 degree
setColorRange([-25 -15]);
% colorize outliers in purple.
cmap = colormap;
cmap(end,:) = [1 0 1];
cmap(1,:) = [1 0 1];
colormap(cmap)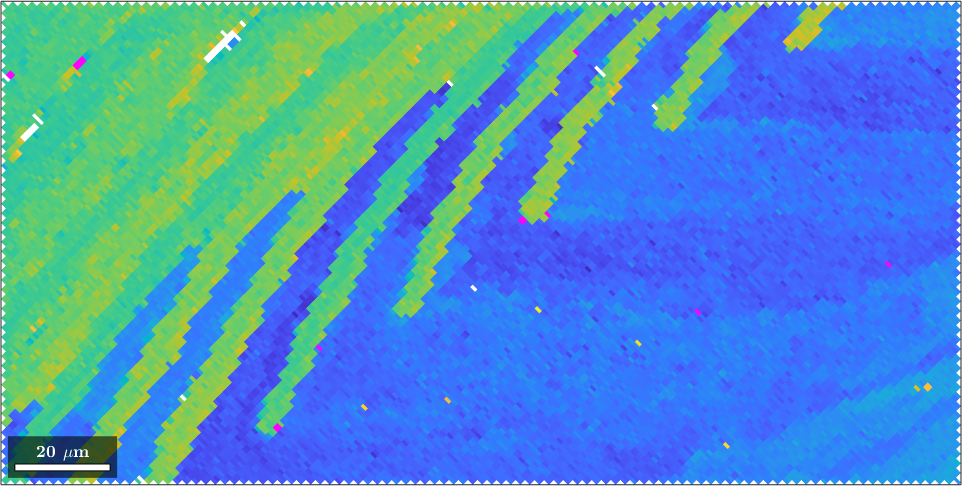
Sharpening the default color coding
Next, we want to apply the same ideas as above to the default MTEX color key, i.e. we want to stretch the colors such that they cover just the orientations of interest.
ipfKey = ipfHSVKey(ebsd.CS.properGroup);
% To this end, we first compute the inverse pole figure direction such that
% the mean orientation is just at the gray spot of the inverse pole figure
ipfKey.inversePoleFigureDirection = mean(ebsd.orientations,'robust') * ipfKey.whiteCenter;
close all;
plot(ebsd,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd.orientations))
We observe that the orientation map is almost completely gray, except for the outliers which appears black. Next, we use the option 'maxAngle' to increase contrast in the grayish part
ipfKey.maxAngle = 7.5*degree;
plot(ebsd,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd.orientations))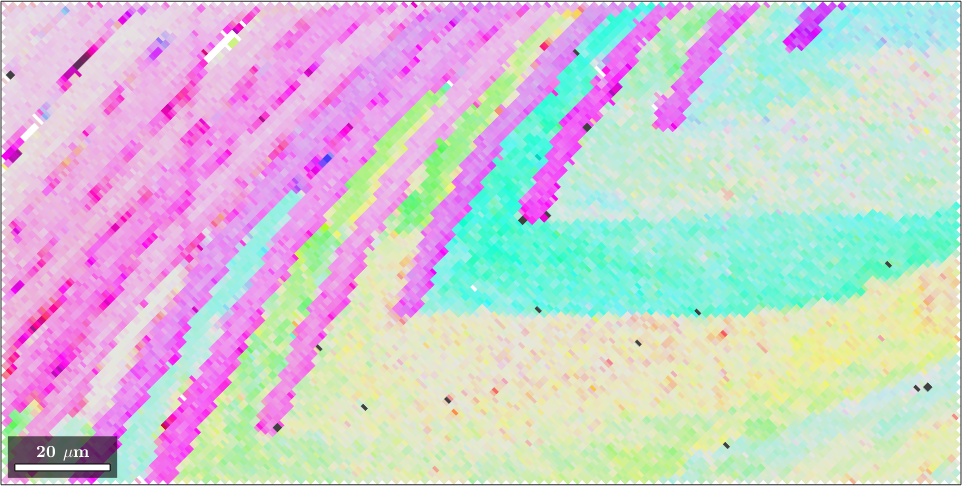
You may play around with the option 'maxAngle' to obtain better results. As for interpretation keep in mind that white color represents the mean orientation and the color becomes more saturated and later dark as the orientation to color diverges from the mean orientation.
Let's have a look at the corresponding color map.
plot(ipfKey,'resolution',0.25*degree)
% plot orientations into the color key
hold on
plotIPDF(ebsd.orientations,'points',10,'MarkerSize',1,'MarkerFaceColor','w','MarkerEdgeColor','w')
hold offI'm plotting 10 random orientations out of 20151 given orientations
observe how in the inverse pole figure the orientations are scattered closely around the white center. Together with the fact that the transition from white to color is quite rapidly, this gives a high contrast.
The axis angle color key
A second option to visualize small orientation deviation, e.g. within a grains is the axisAngleColorKey. In order to demonstrate this color key let us first separate the EBSD into grains.
[grains,ebsd.grainId] = calcGrains(ebsd,'angle',1.5*degree,'minPixel',3);
grains = smooth(grains,5);In order to apply the axisAngleColorKey we need to specify the crystal symmetry and a reference orientation oriRef. Often the meanorientation of the grains is a good choice.
ipfKey = axisAngleColorKey(ebsd);
% use for the reference orientation the grain mean orientation
ipfKey.oriRef = grains.meanOrientation(ebsd('indexed').grainId);
plot(ebsd('indexed'),ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd('indexed').orientations))
hold on
plot(grains.boundary,'lineWidth',4)
hold off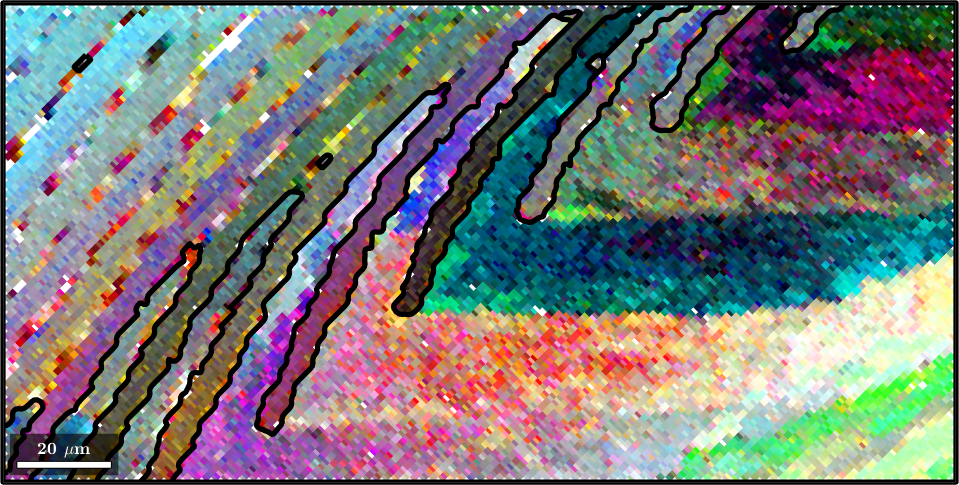
Being able to visualize very small orientation changes gives us better way to observe how EBSD denoising methods work
F = halfQuadraticFilter;
ebsdS = smooth(ebsd,F,'fill',grains);
% use for the reference orientation the grain mean orientation
ipfKey.oriRef = grains.meanOrientation(ebsdS('indexed').grainId);
plot(ebsdS('indexed'),ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsdS('indexed').orientations))
hold on
plot(grains.boundary,'lineWidth',4)
hold off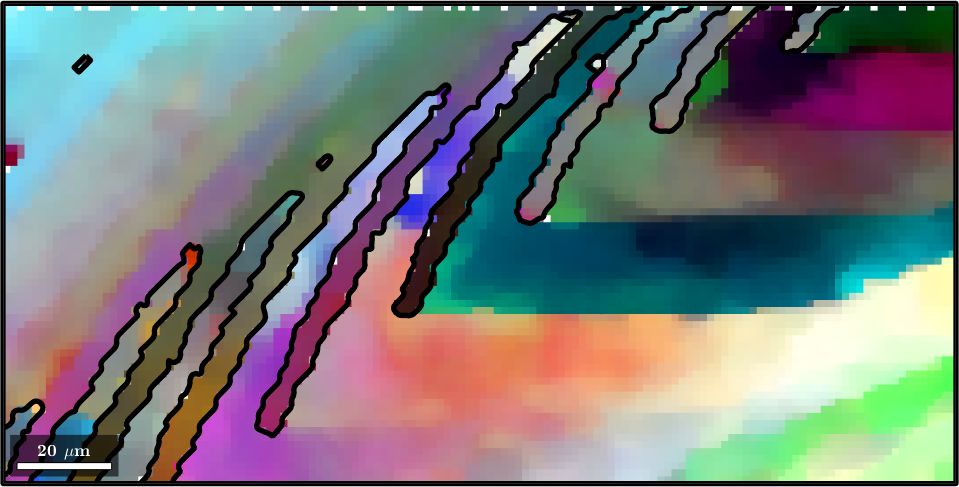
Another application for sharp color keys is the analysis of orientation gradients within grains
mtexdata forsterite silent
% segment grains
[grains,ebsd.grainId] = calcGrains(ebsd('indexed'));
% find largest grains
largeGrains = grains(grains.numPixel > 800);
ebsd = ebsd(largeGrains(1))ebsd = EBSD (y↑→x)
Phase Orientations Mineral Color Symmetry Crystal reference frame
1 1453 (100%) Forsterite LightSkyBlue mmm
Properties: bands, bc, bs, error, mad, grainId
Scan unit : um
X x Y x Z : [14800, 17850] x [0, 1600] x [0, 0]
Normal vector: (0,0,1)When plotting one specific grain with its orientations we see that they all are very similar and, hence, get the same color
% plot a grain
close all
plot(largeGrains(1).boundary,'linewidth',2)
hold on
plot(ebsd,ebsd.orientations)
hold off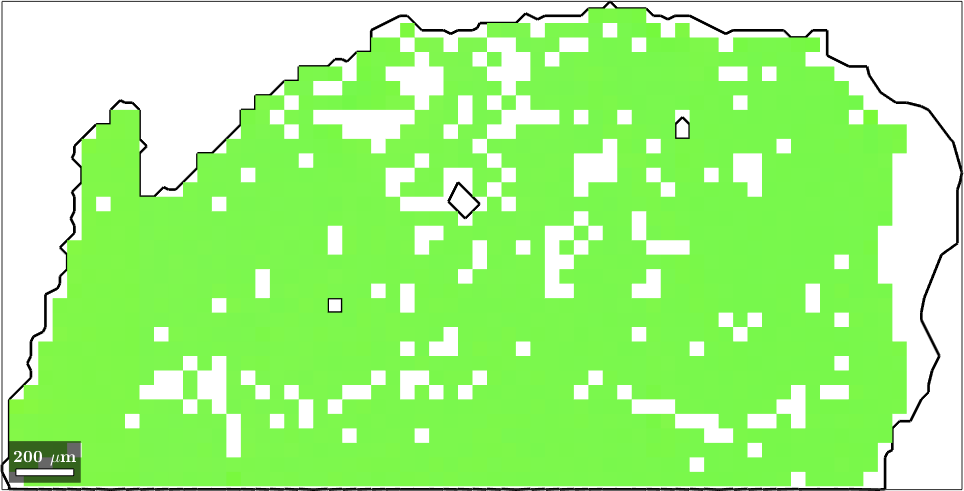
when applying the option sharp MTEX colors the mean orientation as white and scales the maximum saturation to fit the maximum misorientation angle. This way deviations of the orientation within one grain can be visualized.
% plot a grain
plot(largeGrains(1).boundary,'linewidth',2)
hold on
ipfKey = ipfHSVKey(ebsd);
ipfKey.inversePoleFigureDirection = mean(ebsd.orientations) * ipfKey.whiteCenter;
ipfKey.maxAngle = 2*degree;
plot(ebsd,ipfKey.orientation2color(ebsd.orientations))
hold off