hierarchical clustering of rotations and vectors
Syntax
[c,center] = doHCluster(ori,'numCluster',n)
[c,center] = doHCluster(ori,'maxAngle',omega)Input
| ori | orientation |
| n | number of clusters |
| omega | maximum angle |
Output
| c | list of clusters |
| center | center of the clusters |
Example
generate orientation clustered around 5 centers
cs = crystalSymmetry('m-3m');
center = orientation.rand(5,cs);
odf = unimodalODF(center,'halfwidth',5*degree)
ori = odf.discreteSample(3000);odf = SO3FunRBF (m-3m → y↑→x)
multimodal components
kernel: de la Vallee Poussin, halfwidth 5°
center: 5 orientations
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 weight
156.958 109.836 223.608 0.2
9.33344 126.207 190.491 0.2
197.878 76.1995 48.4488 0.2
156.716 113.621 184.888 0.2
151.332 117.797 66.3984 0.2find the clusters and its centers
[c,centerRec] = calcCluster(ori,'method','hierarchical','numCluster',5);visualize result
plot(ori,ind2color(c),'axisAngle')plot 2000 random orientations out of 3000 given orientations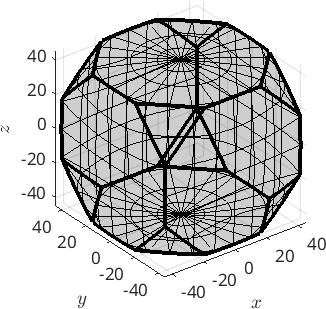
%check the accuracy of the recomputed centers
min(angle_outer(center,centerRec)./degree)ans =
0.3032 0.3298 0.2366 0.5450 0.1580alternative approach to compute the cluster centers
odfRec = calcDensity(ori)
[~,centerRec2] = max(odfRec,'numLocal',5);
min(angle_outer(center,centerRec2)./degree)odfRec = SO3FunHarmonic (m-3m → y↑→x)
bandwidth: 25
weight: 1
ans =
0.4582 0.6089 0.1909 0.8792 0.6571