Spin Tensors
Spin Tensors as Ininitesimal Changes of Rotations
Spin tensors are skew symmetric tensors that can be used to approximate small rotational changes. Lets consider an arbitrary reference rotation
rot_ref = rotation.byEuler(10*degree,20*degree,30*degree)
rot_ref = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
10 20 30 0
and pertube it by a rotating about the axis (123) and angle delta. Since multiplication of rotations is not commutativ we have to distinguish between left and right pertubations
delta = 0.01*degree; rot_right = rotation.byAxisAngle(vector3d(1,2,3),delta) * rot_ref; rot_left = rot_ref * rotation.byAxisAngle(vector3d(1,2,3),delta);
We may now ask for the first order Taylor coefficients of the pertubation as delta goes to zero which we find by the formula
$$ T = \lim_{\delta \to 0} \frac{\tilde R - R}{\delta}
T_right = (rot_right.matrix - rot_ref.matrix)./delta T_left = (rot_left.matrix - rot_ref.matrix)./delta
T_right =
-0.4002 -0.4146 0.7724
0.5727 -0.5873 -0.2035
-0.2484 0.5297 -0.1218
T_left =
-0.5399 -0.6025 0.5816
0.7530 -0.5816 0.1368
-0.2648 0.1140 0.0122
Both matrices T_right and T_left are elements of the tangential space attached to the reference rotation rot_ref. Those matrices are characterized by the fact that they becomes scew symmetric matrices when multiplied from the left or from the right with the inverse of the reference rotation
S_right_L = matrix(inv(rot_ref)) * T_right S_right_R = T_right * matrix(inv(rot_ref)) S_left_L = matrix(inv(rot_ref)) * T_left S_left_R = T_left * matrix(inv(rot_ref))
S_right_L =
-0.0000 -0.5892 0.4501
0.5893 -0.0001 -0.6709
-0.4501 0.6710 -0.0001
S_right_R =
-0.0001 -0.8018 0.5345
0.8018 -0.0001 -0.2672
-0.5345 0.2673 -0.0000
S_left_L =
-0.0001 -0.8018 0.5345
0.8018 -0.0001 -0.2672
-0.5345 0.2673 -0.0000
S_left_R =
-0.0001 -0.9575 0.2758
0.9575 -0.0001 0.0850
-0.2758 -0.0850 -0.0000
A scew symmetric 3x3 matrix S is essentially determined by its entries 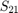 ,
, 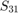 and
and 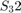 . Writing these values as a vector
. Writing these values as a vector 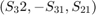 we obtain for the matrices S_right_R and S_left_L exactly the rotational axis of our pertubation
we obtain for the matrices S_right_R and S_left_L exactly the rotational axis of our pertubation
vector3d(spinTensor(S_right_R)) * sqrt(14) vector3d(spinTensor(S_left_L)) *sqrt(14)
ans = vector3d size: 1 x 1 x y z 1 2 3 ans = vector3d size: 1 x 1 x y z 1 2 3
For the other two matrices those vectors are related to the rotatinal axis by the reference rotation rot_ref
rot_ref * vector3d(spinTensor(S_right_L)) * sqrt(14) inv(rot_ref) * vector3d(spinTensor(S_left_R)) * sqrt(14)
ans = vector3d size: 1 x 1 x y z 1 2 3 ans = vector3d size: 1 x 1 x y z 1 2 3
The Functions Log
The above definition of the spin tensor works only well if the pertupation rotation has small rotational angle. For large pertubations the matrix logarithm is the accurate way to compute the skew symmetric matrix, i.e., the spinTensor, of the rotational change between an reference orientation and another orientation.
rot_123 = rotation.byAxisAngle(vector3d(1,2,3),57.3*degree)
S = logm(rot_ref * rot_123,rot_ref)
S = logm(rot_123 * rot_ref,rot_ref,'left')
rot_123 = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
87.091 33.3008 320.221 0
S = spinTensor
rank: 2 (3 x 3)
*10^-2
0 -80.18 53.46
80.18 0 -26.73
-53.46 26.73 0
S = spinTensor
rank: 2 (3 x 3)
*10^-2
0 -80.18 53.46
80.18 0 -26.73
-53.46 26.73 0
Again we may extract the rotational axis directly from the spin tensor
% the rotational axis vector3d(S) * sqrt(14) % the rotational angle in degree norm(vector3d(S)) / degree
ans = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
1.00007 2.00015 3.00022
ans =
57.3000
Alternatively, we may compute the misorientation vector directly by
v = log(rot_ref * rot_123,rot_ref); v * sqrt(14)
log(rot_123 * rot_ref,rot_ref,'left') * sqrt(14)
ans = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
1.00007 2.00015 3.00022
ans = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
1.00007 2.00015 3.00022
The Exponential Function Exp
The exponential function is the inverse of function of the logarithm and hence it takes a spinTensor or a misorientation vector it turns it into a misorientation.
% applying a misorientation directly to the reference orientation rot_ref * rot_123 % do the same with spinTensor exp(S,rot_ref) % do the same with the misorientation vector exp(v,rot_ref)
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
94.0543 29.4353 358.508 0
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
94.0543 29.4353 358.508 0
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
94.0543 29.4353 358.508 0
S = logm(rot_123 * rot_ref,rot_ref,'left'); rot_123 * rot_ref exp(S,rot_ref,'left') v = log(rot_123 * rot_ref,rot_ref,'left'); exp(v,rot_ref,'left')
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
ans = rotation
size: 1 x 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
Now the same with orientations
cs = crystalSymmetry('321') % consider an arbitrary rotation ori_ref = orientation.byEuler(10*degree,20*degree,30*degree,cs) % next we disturb rot_ref by a rotation about the axis (123) mori_123 = orientation.byAxisAngle(Miller(1,2,-3,3,cs),1) % first we multiply from the right ori = ori_ref * mori_123;
cs = crystalSymmetry
symmetry : 321
a, b, c : 1, 1, 1
reference frame: X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
ori_ref = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
10 20 30 0
mori_123 = misorientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
61.8386 40.0064 340.052 0
S_right_L = matrix(inv(rot_ref)) * T_right S_right_R = T_right * matrix(inv(rot_ref)) S_left_L = matrix(inv(rot_ref)) * T_left S_left_R = T_left * matrix(inv(rot_ref))
S_right_L =
-0.0000 -0.5892 0.4501
0.5893 -0.0001 -0.6709
-0.4501 0.6710 -0.0001
S_right_R =
-0.0001 -0.8018 0.5345
0.8018 -0.0001 -0.2672
-0.5345 0.2673 -0.0000
S_left_L =
-0.0001 -0.8018 0.5345
0.8018 -0.0001 -0.2672
-0.5345 0.2673 -0.0000
S_left_R =
-0.0001 -0.9575 0.2758
0.9575 -0.0001 0.0850
-0.2758 -0.0850 -0.0000
make it a vector
vR1 = vector3d(spinTensor(S_right_L)) *sqrt(14) vR2 = inv(rot_ref) * vector3d(spinTensor(S_right_R)) * sqrt(14) lR1 = rot_ref * vector3d(spinTensor(S_left_L)) *sqrt(14) lR2 = vector3d(spinTensor(S_left_R)) * sqrt(14)
vR1 = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
2.51049 1.6841 2.20482
vR2 = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
2.51049 1.6841 2.20482
lR1 = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
-0.317983 1.03184 3.58248
lR2 = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
-0.317983 1.03184 3.58248
logarithm to vector3d
log(ori_ref * mori_123,ori_ref)
log(rot_123 * ori_ref,ori_ref,'left') * sqrt(14)
ans = Miller
size: 1 x 1
symmetry: 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
h 0.2335
k 0.4671
i -0.7006
l 0.7006
ans = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
1.00007 2.00015 3.00022
logarithm to skew symmetric matrix
S = logm(ori_ref * mori_123,ori_ref)
round(vector3d(S))
S = logm(rot_123 * ori_ref,ori_ref,'left')
vector3d(S) * sqrt(14)
S = spinTensor
rank : 2 (3 x 3)
mineral: 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
*10^-2
0 -70.06 46.71
70.06 0 -53.94
-46.71 53.94 0
ans = Miller
size: 1 x 1
symmetry: 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
h 1
k 2
i -3
l 3
S = spinTensor
rank: 2 (3 x 3)
*10^-2
0 -80.18 53.46
80.18 0 -26.73
-53.46 26.73 0
ans = vector3d
size: 1 x 1
x y z
1.00007 2.00015 3.00022
The other way round
S = logm(ori_ref * mori_123,ori_ref); ori_ref * mori_123 exp(S,ori_ref) v = log(ori_ref * mori_123,ori_ref); exp(v,ori_ref)
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
79.3156 43.3785 9.9013 0
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
79.3156 43.3785 9.9013 0
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
79.3156 43.3785 9.9013 0
S = logm(rot_123 * ori_ref,ori_ref,'left'); rot_123 * ori_ref exp(S,ori_ref,'left') v = log(rot_123 * ori_ref,ori_ref,'left'); exp(v,ori_ref,'left')
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
ans = orientation
size: 1 x 1
crystal symmetry : 321, X||a*, Y||b, Z||c*
specimen symmetry: 1
Bunge Euler angles in degree
phi1 Phi phi2 Inv.
74.5565 51.5076 9.61124 0
Complete Function list
| Syntax | |
| Omega = spinTensor(v) | |
| Omega = spinTensor(S) | |
| Omega = spinTensor(rot) | |
| Omega = spinTensor(mori) | |
| Input | |
| S | skew symmetry matrix |
| v | @vector3d |
| rot | @rotation |
| mori | mis@orientation |
| DocHelp 0.1 beta |